All green plants produce sugar (sucrose) through photosynthesis. Table sugar is obtained from sugar cane and sugar beets due to their high sucrose content. Whether produced from cane or beet, the result is the same: pure sucrose. The process of extracting and purifying sugars from sugar cane and sugar beet allows for the production of a large variety of sugars.
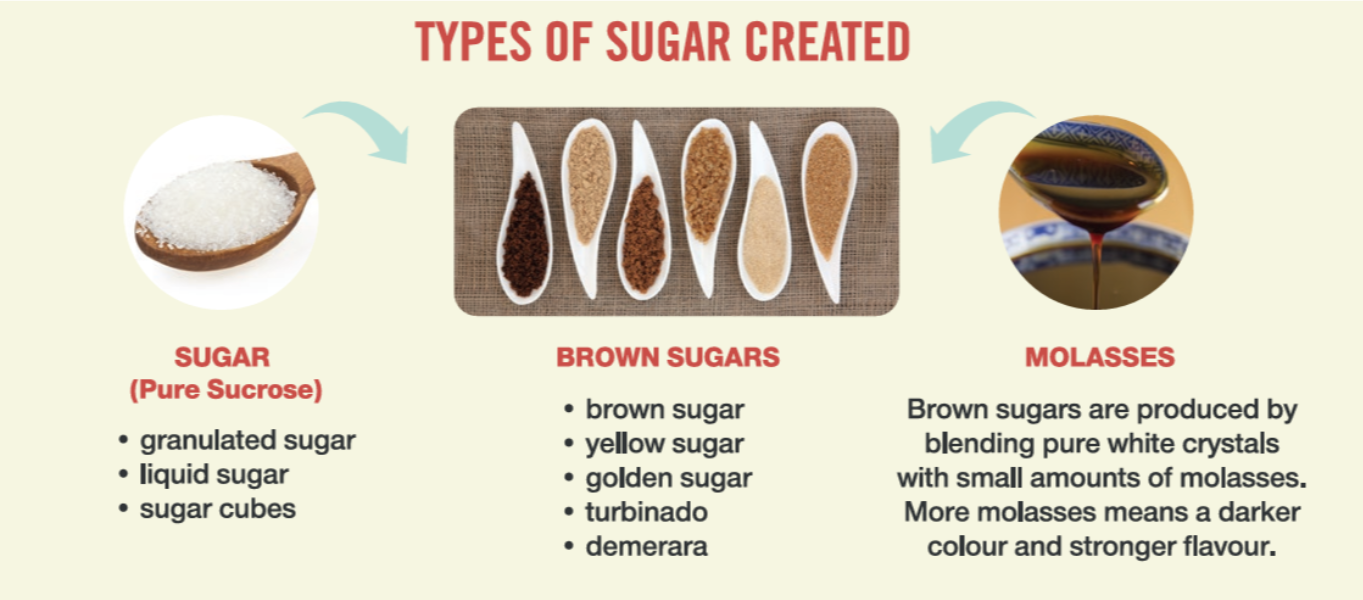
- Sugar. This includes granulated sugar, coarse sugar, superfine sugar, pearl sugar, liquid sugar, and liquid invert sugar.
- Specialty Sugars. This includes brown sugar, icing sugar, Demerara-style sugar, Muscovado sugar, Turbinado-style sugar, organic sugar, golden syrup, and molasses.
- Other Sugars. This includes raw sugar and evaporated cane juice.
Sugar
Canada's Food Compositional Standards require that "sugar" meets the standard of at least 99.8% pure sucrose. The purification process can produce different crystal sizes, as well as liquid sugars. These characteristics allow sugar to perform a variety of functions in food products, in addition to providing a sweet taste.
The following table lists different types of sugars and sugar-based products. Alternative names provided may not be commonly used in Canada.
| Type of Sugar | Description | May Also be Called | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
Granulated sugar
|
Naturally white, pure sucrose The most common form of refined sugar |
Refined sugar Sucrose Table sugar White sugar |
General household use (tea, coffee, home recipes) Performs a variety of functions when added to breads, baked goods, frozen dairy products, jams/jellies, candies, packaged foods |
Coarse sugar
|
Granulated sugar having a larger crystal size Highly resistant to colour change and breakdown (into glucose and fructose) at high temperatures |
Used in making fondants, confections and liquors | |
Superfine sugar
|
Crystal size is the finest of all the types of granulated sugar |
Bar sugar Berry sugar Castor sugar Extra fine sugar Fruit sugar Instant dissolving sugar Ultrafine sugar |
Excellent for sprinkling over fruit or cereals, or in creamed mixtures, meringues and baking Used commercially in powdered preparations, in the preservation of fruits, and dissolves easily in cold beverages |
Pearl sugar
|
Lumps of refined sugar particles |
Decorative sugar Sanding sugar |
Used mainly in the baking and confectionery industries to sprinkle on top of baked goods |
Liquid sugar
|
Granulated white sugar dissolved in water |
Liquid sucrose Sucrose syrups |
Used commercially in beverages, jams, candy, ice cream, syrups, and cooked fondants (i.e. fudge) Not available for purchase by consumers |
Liquid invert sugar
|
Mixture of glucose and fructose when sucrose is broken down in solution |
Used commercially, primarily in soft drinks Also used in confectionery, canning and baking Not available for purchase by consumers |
Specialty Sugars
| Type of Sugar | Description | May Also be Called | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
Brown sugars
|
White moist granulated sugar blended with small quantities of pure sugar syrups (molasses) that are selected for colour and taste Colour ranges from a light yellow to dark brown The differences in colour and flavour between different brown sugars depend on the amount of molasses present - the more molasses, the stickier the crystals, darker the colour and stronger the flavour Sugar refiners can produce brown sugar from boiling refinery cane syrups until brown sugar crystals form, or by blending molasses syrup with white sugar crystals |
Brilliant yellow sugar Dark brown sugar Golden yellow sugar Light yellow sugar Soft sugar Yellow sugar |
Used in baked goods, dry mixes, meat glazes, and condiments |
Icing sugar
|
Finely ground (powdered) granulated sugar, which contains approximately 3% cornstarch (gluten-free), an anti-caking agent to prevent clumping |
Confectioner's sugar Fondant sugar Fondant icing sugar Powdered sugar Pure icing sugar Super icing sugar |
Used in special glazes, icings for cakes and doughnuts, and some sweet pastries |
Demerara-style sugar
|
A specialty light brown sugar, with large golden crystals that are slightly sticky due to a molasses coating | Brown sugar |
Used as a specialty item for household baked goods Often used in tea, coffee, or on top of hot cereals |
Muscovado sugar
|
Made by crystallization of dark syrups (similar to Demerara-style) Crystals are slightly coarser and stickier in texture than regular brown sugar Produced at an early stage of the refining process where not all plant pigments and flavours are removed Colour ranges from light to dark brown and has a strong molasses taste |
Barbados sugar | Specialty product used on cereal, in puddings and fruit cakes, in marinades and sauces, or in coffee and tea |
Turbinado-style sugar
|
A semi-refined specialty brown sugar that has been partially purified (double washed) for human consumption Molasses coating gives it a golden colour and mild caramel taste |
Often found under the brand names "Plantation sugar" or "Sugar in the Raw" |
Used for hot beverages Can be used as a finishing touch for cookies, pastries, and cobblers Often found in restaurants and specialty shops |
Organic sugar
|
Grown where sustainable agriculture is practiced, for example crop rotation, effective soil rotation, effective soil conversation, and natural biological pest control (no pesticides or artificial fertilizers) Made from cane syrups that are filtered and cleaned using only natural herbal extracts and vegetable purifiers |
Used in place of granulated white sugar, for example, in cooking or baking, on cereal, and in coffee, tea and other beverages | |
Golden syrup
|
Golden-coloured syrup containing sucrose and invert sugar (sucrose broken down into its two component sugars, glucose and fructose) Made from selected blended refinery cane syrups, which are thickened by evaporation |
Refiner's syrup Refined sugar syrup |
Used in recipes as a syrup topping |
Molasses
|
Dark coloured syrup that is a by-product of the sugar cane and sugar beet refining processes Generally, molasses from refineries requires further processing to meet the food grade standard to be packaged and sold in the grocery store |
Table or Fancy molasses Refiner's or Blackstrap or Cooking molasses |
Baking, yeast production Rum or other alcohol production as a fermentable carbohydrate |
Other Sugars
| Type of Sugar | Description | May Also be Called | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
Raw Sugar
|
In Canada, “raw sugar” refers to the partially purified cane sugar shipped here for further refining. It looks like soft brown sugar but contains impurities that require it to be refined in order to meet Canadian standards for health and hygiene | Not to be confused with so-called "raw sugar" or "sugar in the raw" packaged and sold in stores, which are types of specialty sugar, such as turbinado | This product is not sold to consumers |
Evaporated Cane Juice
|
Misleading term to describe lightly golden, granulated cane sugar with a slight molasses flavour Processed from milled sugar cane through a single-crystallization process |
Cane sugar Turbinado sugar Organic cane sugar See: US FDA Guidance that the ingredient should be declared on food labels as a sugar using more truthful non-misleading descriptors |
Used as a sweetening agent similar to light brown sugar, turbinado sugar and other specialty sugars that retain more molasses Used in baked goods, on top of hot cereal, and to sweeten beverages, smoothies, or plain yogurt |
For more information, additional resources include:
- Infographic - Types of Sugars and Sweeteners


















